Common Nissan Vehicle Problems that affect the CVT transmission and How to Diagnose Them: A Mechanic’s Guide
As a mechanic, you’re likely to encounter a wide range of issues in Nissan vehicles, including engine misfires and CVT transmission problems. To ensure the longevity of any new CVT transmission, including TD REMAN’s remanufactured CVT transmissions, it’s essential to perform a full vehicle scan to identify the “root causes” of the original CVT failure.
Identifying these “root causes” is crucial because it helps you understand what led to the original transmission’s breakdown. This allows you to address the underlying issues that could otherwise cause the new CVT to fail prematurely. By pinpointing potential problems—whether it’s a faulty sensor, worn engine component, or electrical issue—you can make sure the new TD REMAN remanufactured CVT operates smoothly and lasts much longer.
Additionally, properly addressing these root causes protects your customer’s warranty by preventing the same failures from happening again. With this proactive approach, you not only increase repair accuracy but also ensure customer satisfaction and prevent costly future repairs. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most frequent Nissan issues and how you can identify and resolve them to protect your new transmission.
-
Engine Misfires
- Common Codes: P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire), P0301-P0308 (Specific Cylinder Misfires)
- Worn out spark plugs, ignition wires, coil(s), distributor cap and rotor (when applicable), Incorrect ignition timing, Vacuum leak(s), Low or weak fuel pressure, improperly functioning EGR system, Defective Mass Air Flow Sensor, Defective Crankshaft and/or Camshaft Sensor, Defective Throttle Position Sensor, Mechanical engine problems (i.e.—low compression, leaking head gasket(s), or valve problems).
- Symptoms: Rough idle, lack of power, engine stalling, increased fuel consumption, and in severe cases, engine damage.
- Solution: Misfires are often caused by worn spark plugs, ignition coil issues, or fuel delivery problems. Start by checking the spark plugs and ignition coils and perform a fuel system test.
-
Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF) Issues
- Common Codes: P0101 (MAF Sensor Circuit Range/Performance), P0102 (MAF Sensor Low Input), P0103 (MAF Sensor High Input)
- Large vacuum leaks, Split Intake Air Boot or PCV Hose, Defective intake manifold gaskets, Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF), Mass Air Flow Sensor circuit and or wiring problems, Defective Barometric Pressure Sensor, Dirty or contaminated Mass Air Flow Sensing wire or filament, PCM software needs to be updated.
- The Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF) Sensor is unplugged, or the wiring is damaged, Loose or corroded electrical terminals in the MAF Sensor circuit, Faulty MAF Sensor
- Symptoms: Poor acceleration, rough idle, engine stalling, and reduced fuel economy.
- Solution: A faulty MAF sensor can cause the engine to miscalculate the air-fuel mixture. Inspect and clean the MAF sensor or replace it if damaged.
-
Ripped Air Duct Hose to the Throttle Body
- Common Codes: P0171 (System Too Lean – Bank 1), P0174 (System Too Lean – Bank 2)
- Control module software needs to be updated, Vacuum leaks (intake manifold gaskets, vacuum hoses, PCV hoses, etc.), Mass air flow sensor, plugged fuel filter or weak fuel pump, Plugged or dirty fuel injectors.
- Symptoms: Lean air-fuel mixture, rough idle, poor acceleration, and engine stalling.
- Solution: Check for tears or cracks in the air duct hose between the MAF sensor and throttle body. Replace the hose to prevent unmetered air from entering the engine, which can cause these issues.
-
Crankshaft and Camshaft Sensor Issues
- Common Codes: P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit), P0340 (Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit)
- Harness or connectors Crankshaft position sensor (POS) circuit is open, damaged, or shorted.
- Symptoms: Difficulty starting, stalling, engine misfires, poor acceleration, and irregular engine behavior.
- Solution: These sensors are crucial for the engine’s timing. Inspect both sensors and wiring for damage, and replace faulty sensors to restore engine performance.
-
ABS Problems (Anti-lock Braking System)
- Common Codes: C1145 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Failure), C1142 (ABS Pump Motor Relay Circuit)
- Faulty brake fluid sensor harness is open or shorted. A poor electrical connection. A faulty brake lamp switch, ABS actuator and or electrical unit.
- Symptoms: ABS warning light on, decreased braking performance, potential wheel lockup during hard braking.
- Solution: Check the wheel speed sensors, ABS wiring, and the ABS control module. Replace any damaged sensors or wiring to restore proper ABS function.
-
Wiring Problems
- Common Codes: Various codes depending on the affected component (e.g., P0600, P0601, P0602, P0603, P0605 for PCM wiring failure reference voltage issue).
- Defective PCM (Power Train Control Module), Defective PCM data bus wiring/connections, Defective PCM data bus ground circuit(s), Defective PCM or other control module-controlled output devices, Defective CAN bus communication. Lack of proper voltage to the PCM, Defective PCM memory module, Defective PCM ground circuit(s), Defective PCM controlled output devices. Powertrain Control Module (PCM) failure, Wiring issue. Lack of proper voltage to the Keep Alive Memory connection on the PCM, Defective PCM Keep Alive Memory Module (KAM), Defective PCM ground circuit(s), Defective PCM controlled output devices
- Symptoms: Sensor malfunctions, communication errors between control modules, erratic performance of vehicle systems.
- Solution: Trace wiring related to the error code for any signs of damage, fraying, or loose connections. Repair or replace the wiring as needed to resolve electrical issues.
-
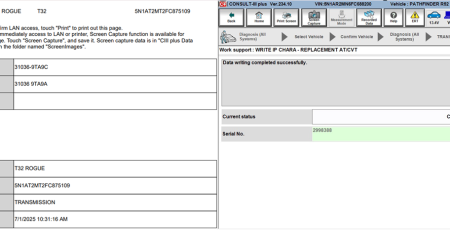
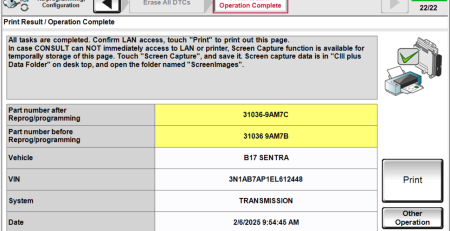
Wrong or Defective Transmission Control Module (TCM)
- Common Codes: U1000 (Cannot Communicate with TCM / Class 2 Communications Failure), U0101 (Lost Communication with TCM)
- When ECM is not transmitting or receiving CAN communication signal of OBD (emission related diagnosis for 2 seconds or more.
- Symptoms: No “Park” or “Neutral” displayed on dashboard. Shifting problems, inability to change gears, stalling, or transmission slippage.
- Solution: A defective or incorrectly installed TCM can cause major transmission issues. Replace the TCM and reprogram it as required by Nissan specifications to ensure optimal performance. Harness or connectors (CAN communication line is open or shorted).
Conclusion
Efficiently diagnosing Nissan vehicle problems starts with understanding the most common trouble codes and their root causes. This is essential for protecting your TD REMAN remanufactured CVT transmission and avoiding costly rework due to premature failures. By taking a methodical approach to address issues like engine misfires, MAF sensor malfunctions, and ABS problems, you can greatly extend the life of your customer’s CVT transmission.
By thoroughly diagnosing and fixing the original causes of failure, you can prevent the need for your customer to return with complaints about their new transmission failing again. This not only ensures a longer-lasting CVT but also helps you avoid upset customers, protect your reputation, and build trust by demonstrating reliability with a first-time fix. Proper diagnosis and resolution keep your shop efficient, and customers satisfied, ultimately reducing the risk of rework and costly returns.
Pro Tip: Stay ahead of potential issues by regularly checking components like air duct hoses, wiring, and sensor functionality during routine inspections. A proactive approach not only prevents bigger problems but also positions your shop as a reliable and knowledgeable repair center for Nissan vehicles.
By incorporating these strategies into your workflow, you’ll enhance your shop’s reputation for diagnosing and fixing Nissan issues quickly and efficiently.
https://www.autonationnissanchandler.com/service/obd-ii-trouble-codes.htm